AI video recognition breaks video into individual frames, analyzing them through neural networks to identify objects, faces, and actions. The technology combines CNNs for spatial analysis with RNNs for understanding movement over time. Your phone doesn’t magically know your face—it’s comparing pixels to learned patterns at lightning speed. Think digital eyes that process visual data in milliseconds. The system tracks movement, predicts actions, and makes decisions that seem almost human. Keep exploring to uncover the full technological marvel.

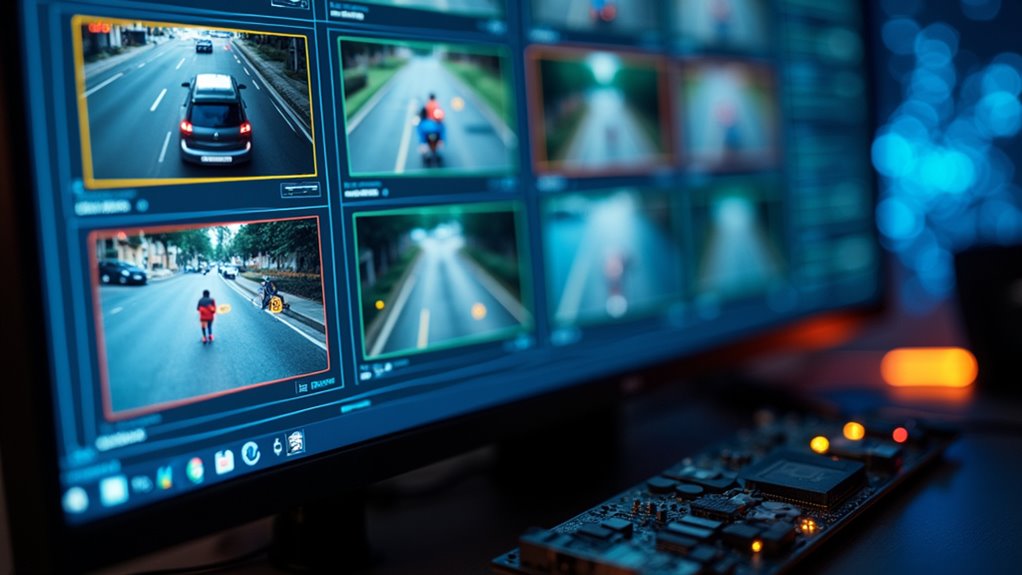
While you’ve likely encountered AI video recognition technology in your daily life, you might not realize how it’s quietly transforming everything from your smartphone’s face access to city-wide surveillance systems. This technology isn’t magic—it’s a sophisticated combination of computer vision and deep learning that processes video content to detect, track, and identify objects and activities in real time. Every time you access your phone with your face, AI is rapidly analyzing your features against stored data.
At its core, AI video recognition relies on object tracking and scene analysis to make sense of visual information. Think of it as having thousands of digital eyes that never blink, constantly monitoring pixel changes across frames. The system doesn’t “see” a car—it recognizes patterns of pixels that match its learned concept of “car.” When that car moves, object tracking algorithms follow it, predicting its path and understanding its relationship to other elements in the scene. Not impressed yet? Consider that this happens in milliseconds across multiple objects simultaneously.
AI video recognition doesn’t see objects—it tracks pixel patterns matching learned concepts in milliseconds across multiple elements simultaneously.
These systems depend on complex neural networks, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for spatial analysis and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) for temporal understanding. The real workhorses, though, are 3D CNNs that analyze both space and time relationships—crucial for distinguishing between someone waving hello versus swinging a baseball bat. Training these models requires massive datasets and computational power that would make your gaming PC weep. The process often requires professional assistance with frame-by-frame annotation using specialized techniques to create effective training datasets.
The applications extend far beyond cool smartphone tricks. Autonomous vehicles use this technology to avoid collisions, retail stores analyze shopping patterns, and healthcare facilities monitor patients for falls or distress. Similar to medical imaging analysis in healthcare, these systems can extract meaningful data from visual content to identify potential problems before they become critical. Implementing successful AI video recognition systems requires batch processing to handle high volumes of video content efficiently while conserving computational resources.
The challenges remain significant—lighting changes, camera angles, and processing speed all present hurdles. Despite these obstacles, AI video recognition continues advancing rapidly, processing our visual world in ways that were science fiction just a decade ago.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Privacy Concerns Exist With AI Video Recognition?
AI video recognition presents significant privacy challenges.
Facial recognition capabilities can identify individuals without consent, potentially enabling unwanted tracking. Data security concerns arise from the collection and storage of personal information, which could be vulnerable to breaches or misuse.
The technology also raises questions about surveillance overreach, algorithmic bias, and the lack of robust regulatory frameworks. Companies implementing these systems must balance security benefits with fundamental privacy rights.
Can AI Video Recognition Work Without Internet Connectivity?
Yes, AI video recognition can absolutely work without internet connectivity.
Through offline processing, systems can analyze videos entirely on local devices—no Wi-Fi required. Edge computing technology makes this possible by running AI algorithms directly on cameras or nearby hardware rather than sending everything to cloud servers.
This approach not only enhances privacy (your video data stays put) but also reduces latency since there’s no waiting for data to travel across networks.
How Much Computing Power Is Required for Real-Time Recognition?
Real-time video recognition demands serious computing muscle.
Hardware requirements include at least 4 CPU cores, 8GB VRAM (16GB is better), and RAM that’s double your total VRAM.
NVIDIA GPUs with Tensor Cores are the gold standard for this work.
The processing power needed increases with video resolution, recognition accuracy targets, and the complexity of objects being tracked.
Without sufficient horsepower, your system will stutter—and nobody wants choppy AI performance.
What’s the Typical Error Rate for Different Lighting Conditions?
Error rates in AI video recognition vary dramatically due to lighting impact. In low-light conditions, errors increase by up to 20%, while well-lit environments greatly improve accuracy.
The error variance is substantial—harsh lighting distorts features, while soft, diffused lighting enhances recognition. Systems trained on diverse lighting scenarios perform better, but real-world deployment still presents challenges.
Adaptive algorithms and real-time processing adjustments help mitigate these issues, though perfect accuracy remains elusive across all lighting conditions.
Can AI Recognition Systems Be Fooled by Disguises?
Yes, AI video recognition systems can definitely be fooled by disguises.
Facial alterations like makeup, prosthetics, and accessories can greatly impact recognition accuracy. The disguise effectiveness varies based on the system’s sophistication—consumer-grade systems are more easily tricked than advanced security implementations.
Simple masks, strategic makeup patterns, and even certain hairstyles can confuse AI algorithms by altering key facial reference points.
That’s why cutting-edge systems now incorporate liveness detection and multiple verification methods to combat such deception tactics.